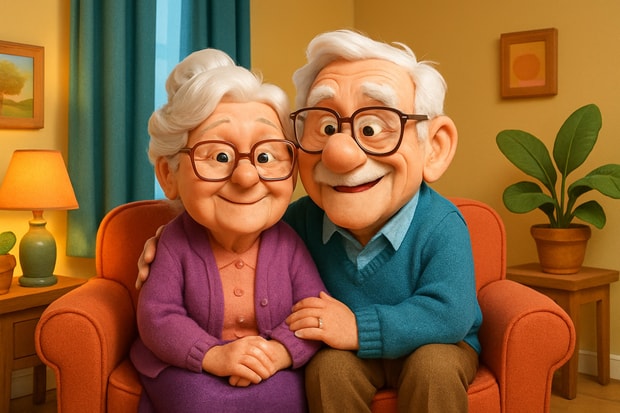
Optional State Supplementation (OSS), also referred to as State Supplementary Payments (SSP), in coordination with the federal Supplemental Security Income (SSI), provides financial assistance for low-income older adults, blind, and disabled individuals in the United States.
Services and Benefits
OSS/ SSP services are usually direct cash payments that aim to cover basic living expenses.
- Increased Cash Assistance
- A higher monthly income than Federal SSI, allowing eligible individuals to afford housing, food, utilities, and clothing.
- Support for Specific Living Arrangement
- Most OSS programs cover residential care in assisted living, adult family care homes, residential care communities, and mental health residential treatment communities.
- Reduced Burden on Individuals/ Families
- OSS provides additional financial support, helping beneficiaries with their financial burdens.
- Alternative to Institutional Care
- OSS helps older adults from nursing homes, especially those with a lower level of care needed.
Although OSS is not a Medicaid program, some states allow recipients to be eligible for Medicaid.
Eligibility
- Characteristics
- Applicants must be 65+, blind, or disabled, as per the federal guidelines.
- Low Income
- Most states follow the federal SSI income limit of 125% of the federal Poverty Guidelines for SSI.
- Although some states may have higher income limits for those who are not eligible for federal SSI.
- Asset Limit
- Individual applicants have a $2,000 asset limit, while couples have $3,000.
- Residency
- Applicants must be residents of the state they are applying for OSS.
- Living Arrangement
- Those living in a residential care home, including assisted living and adult foster care, may receive higher benefits compared to those living independently at home, depending on the state.
- Functional Need
- Those needing additional support for activities of daily living (ADLs) and those who require assistance for physical or mental conditions are subject to assessment.
- Application Process
- For states administered by SSA, application to federal SSI is also an application for OSS. While in state-administered programs, residents should apply to the state’s social services or human resources department.